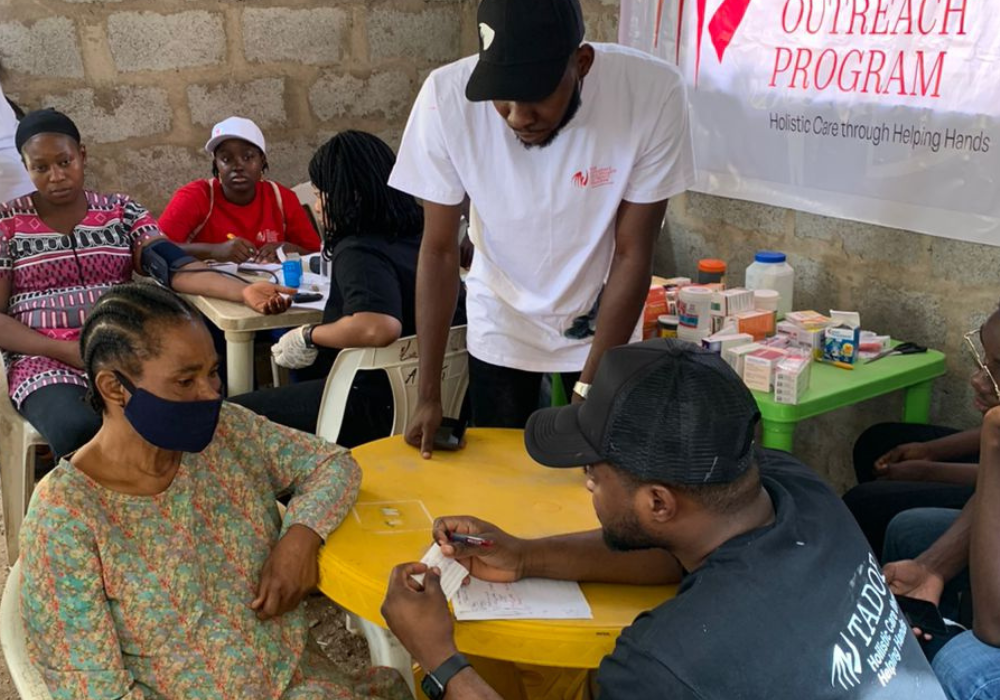
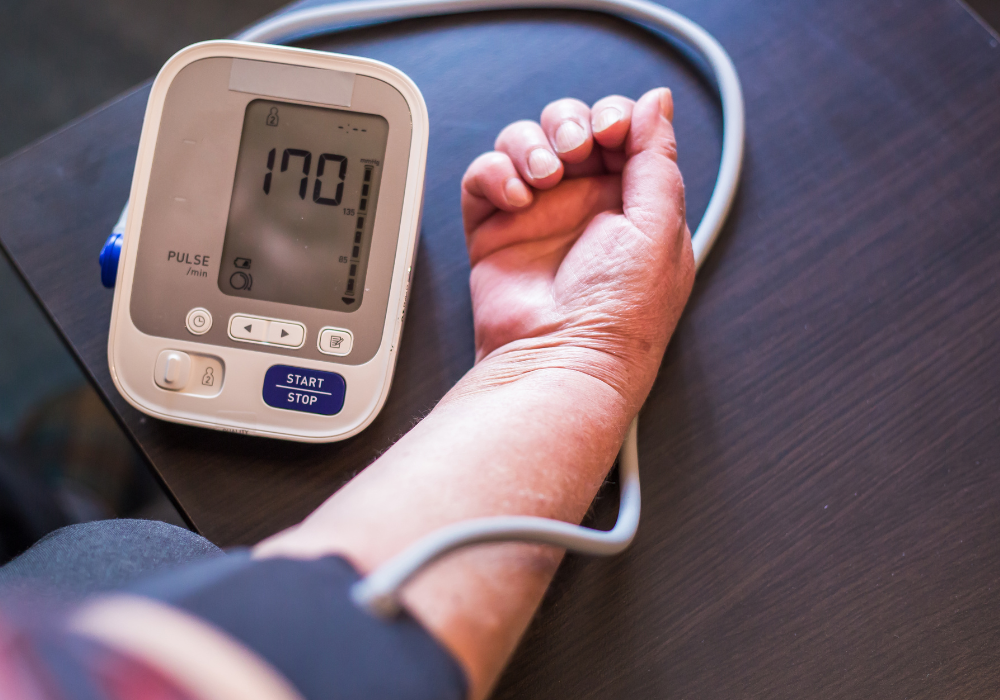
Hypertension, often referred to as high blood pressure, is a common but potentially serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, hypertension is often dubbed the “silent killer” because it typically presents with no symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage. In this blog post, we delve into the importance of understanding hypertension, its risk factors, and strategies for prevention and management.
What is Hypertension?
Hypertension occurs when the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. Over time, this increased pressure can damage blood vessels and organs, leading to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and vision loss. Blood pressure is measured using two numbers: systolic pressure (the pressure when the heart beats) and diastolic pressure (the pressure when the heart rests between beats). A blood pressure reading of 130/80 mmHg or higher is considered hypertensive.
Risk Factors for Hypertension
While hypertension can affect anyone, certain factors increase the risk of developing the condition. These include:
1. Age: The risk of hypertension increases with age, with adults over 65 being particularly vulnerable.
2. Family History: Hypertension tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the condition.
3. Unhealthy Lifestyle: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can all contribute to hypertension.
4. Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the workload on the heart and raises blood pressure.
5. Chronic Conditions: Medical conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, and sleep apnea can increase the risk of hypertension.
Prevention and Management Strategies
While hypertension cannot always be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to lower their risk and manage the condition effectively:
1. Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, along with regular exercise and weight management, can help prevent and control hypertension.
2. Limit Sodium Intake: Reducing sodium intake by minimizing processed and high-sodium foods can lower blood pressure.
3. Manage Stress: Stress can contribute to hypertension, so finding healthy ways to manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and hobbies is essential.
4. Regular Monitoring: Regular blood pressure checks are crucial for early detection and management of hypertension. Individuals with hypertension may need to monitor their blood pressure at home and keep track of readings.
5. Medication: In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to control hypertension, and medication may be necessary. It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations and take prescribed medications as directed.
Conclusion
Hypertension is a significant public health concern with far-reaching consequences if left untreated. By understanding the risk factors, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and working closely with healthcare providers to manage the condition, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of complications associated with hypertension. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to safeguarding your health against the silent threat of hypertension.